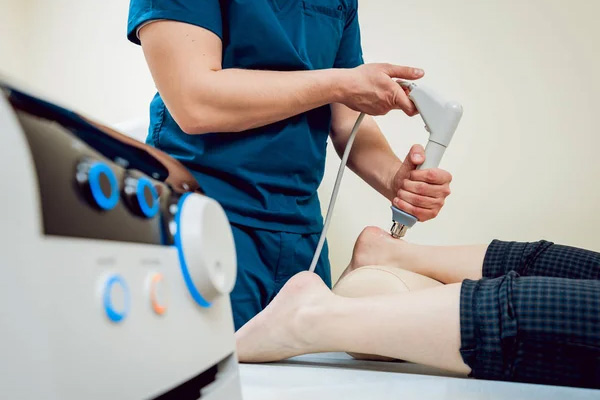
To achieve the maximum result, we use the Masterpuls MP200 shockwave therapy device (Manufacturer: Switzerland).
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment method that utilizes short bursts of acoustic waves directed at stimulating enhanced blood circulation (increased by approximately 10 times). This, in turn, encourages the growth of new blood vessels (neoangiogenesis) and the formation of new collagen structures in the areas of bone, connective, and muscle tissue damage. By targeting the area of inflammation (injury), we enhance the influx of nutrients (stimulating regeneration) and expedite the drainage (dissolution of calcium deposits) of by-products that form during chronic inflammation, improving local metabolism, tissue elasticity, and tolerance to injuries. Shockwave impulses, with a frequency ranging from 1 to 15 Hz and a force of 1.0 to 5.0 bars, are applied to the pathological area. Before commencing the treatment course, the patient must undergo an examination by an orthopedic trauma specialist or with the referral of a doctor.
In summary, shockwave therapy (SWT) entails:
- Stimulating local blood circulation and collagen production (strengthening new collagen fibers).
- Promoting lymphatic flow.
- Breaking down and eliminating calcifications.
- Relieving muscle spasms (trigger points).
Indications for SWT:
- Plantar fasciitis (heel spur).
- Lateral and medial epicondylitis.
- Tendonitis (patellar tendonitis, quadriceps tendonitis).
- Achilles bursitis, Achilles tendon enthesopathy.
- Shoulder scapular periarthritis.
- Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder.
- Inflammatory processes in joint osteoarthritis (knee, hip, shoulder, and ankle joints).
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head (in early stages, before the anatomical structure of the bone is compromised).
- Osgood-Schlatter disease.
- Metatarsalgia of the foot.
- Slow-consolidating fractures of any localization (even with the presence of metal fixators).
- Myofascial syndromes, myositis of any localization.
- Spinal osteochondrosis in remission.
- Tunnel syndromes.
- Tenosynovitis (De Quervain's disease, creaking tendonitis of the forearm).
- Post-traumatic joint contractures.
- Neurodystrophic syndrome.
Contraindications:
- Infectious processes, skin inflammatory processes in the procedure area.
- Oncological diseases.
- Thrombophlebitis (when performing procedures on the affected limb).